Driverless Car: A Thing of the Future? Terms and technologies you need to know!
What? Is that even possible? Will the car be secure? What rules will the car follow? Who will be held responsible if the car collides and if the passenger lives are at risk? Is it trustworthy? These might be some of the questions that arise in your mind when I say driverless car. The answer is pretty simple to that. The car will be safe, when:
* You don’t meddle with the “intelligent” system inside.
* The manufacturer provides a relatively secure system
* The system should be closed source, instead of Open Source.
Open source means that a programmer can change the coding inside the system and doesn’t need permission from the manufacturer- very much like Android. Whereas the close source means that unless the manufacturer or the programmer doesn’t grant permission, the programmer cannot pretty much screw with the system. That is like Windows Phone and iOS. The person with the authority has to change the system seeing the advantages and disadvantages.

Manufacturers who are researching with Autonomous vehicles:
They vary from a wide range of known manufacturers to unknown or startups as well. They include BMW, GM, Audi, Mercedes, Volkswagen, and so on. Now, all this has a starting point. It started with Sebastian Thrun in 2005 – during DARPA challenge where he designed a driverless car that drove past tough terrains to finish the track and also got him $2 million cash prize.
In 2008, Google hired Thrun to develop Google’s Driverless car and the project was officially started in 2010. The technologies involved are very expensive or A-class and if you manage to mess with that, then it means that you will have a very high repairing cost as well. Now, with this development, the big companies got their egos hurt and they also started working on autonomous cars.
The quest on how this challenge came about is rather sad. But do hear it in Thrun’s voice.
This is how the Google car works. Check out the video below
Technologies involved:
This is a very large topic, and I don’t have the time nor the patience to get with all the technologies involved. If you are very much interested, I request you to aid the help of our dear friend, the Internet and our close buddy Google.
Adaptive Cruise Control
This is the term referring to the process of control in which the vehicle controls itself from going in to the adjacent lane and will either warn the driver or will go straight into action.

Lane Keeping Assistance and Lane Centering
These two terms go hand in hand. The System which helps in identifying whether you change to the other lane or in thee likes is the lane keeping assistance system. The Lane centering is the part in which you go in the center of the lane. This system will only work when there are lane markings present. And will only actuate above speeds of 65kmph. This will definitely not work in a country like India where the traffic is just horrible. But we don’t know. A new comer might get this system up working with all his might and hard work and get it in India (A miracle maybe!)
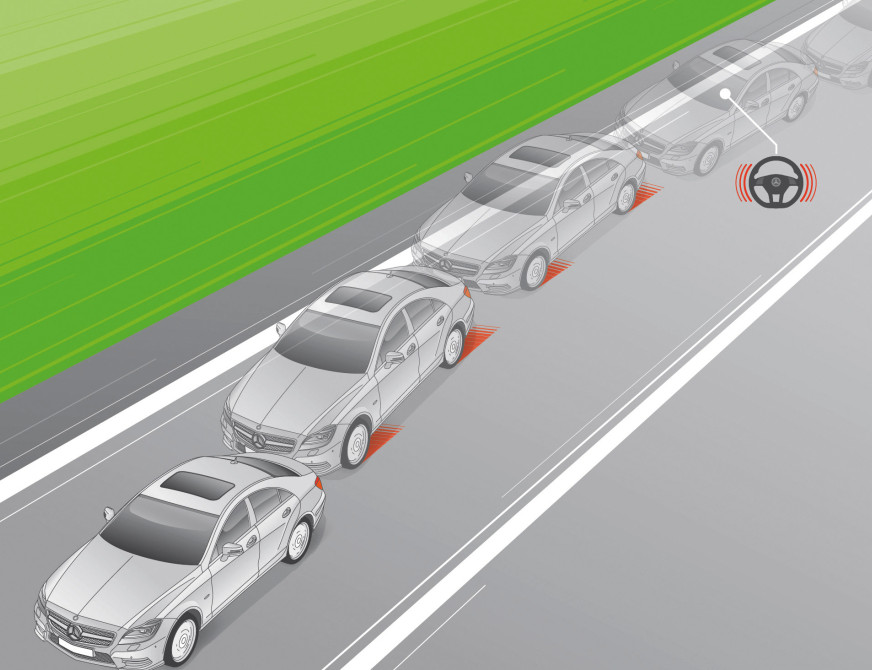
For the beginner level, you have the brake assist and the steering assist on. You can turn it off later. Cameras are placed either on the headlights or the rear view mirrors on the sides and they help in keeping a watch of the lanes. We did cover this in detail in a previous article.
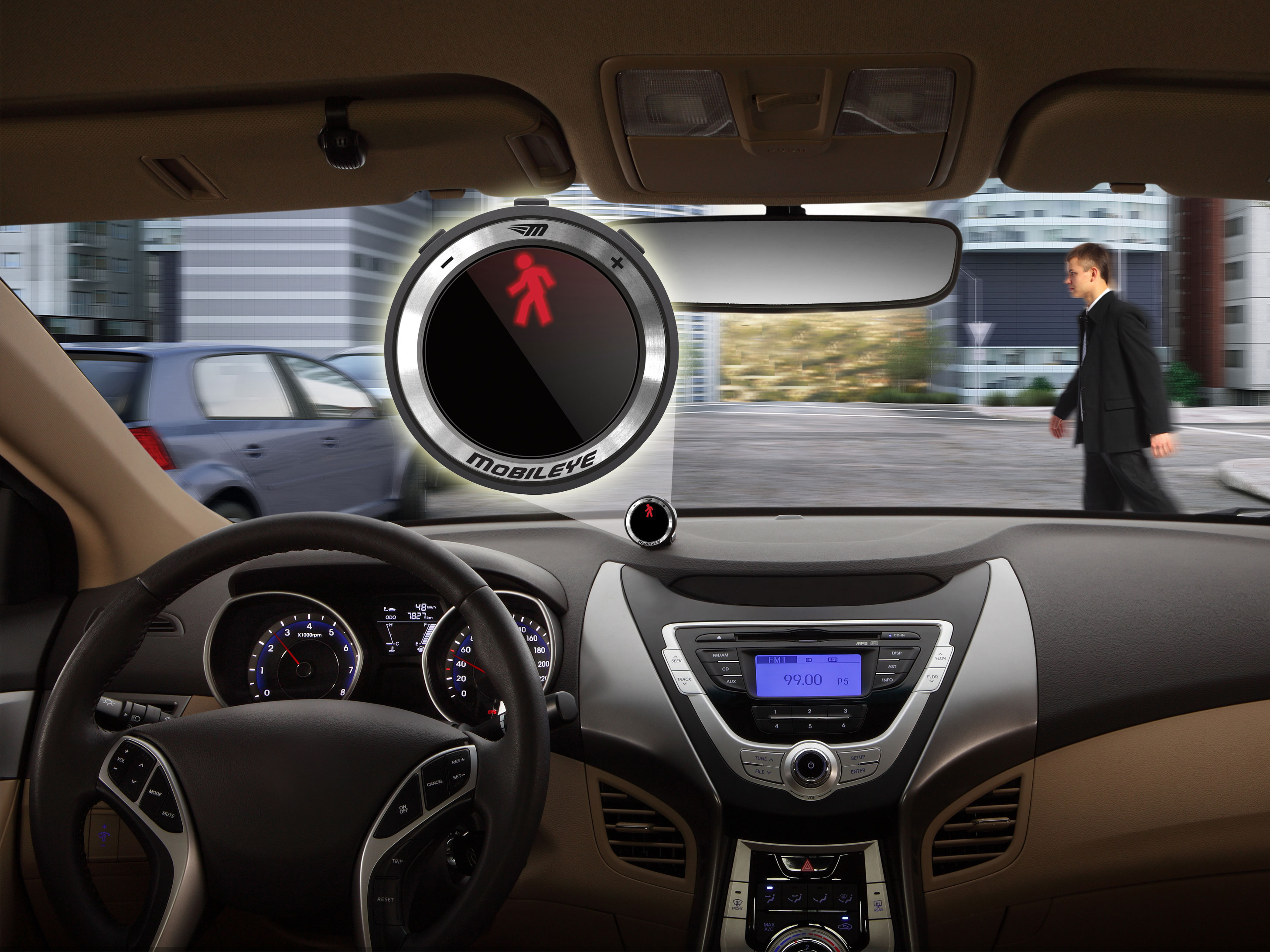
SONAR or RADAR Assist (Obstacle Detection/Collision Avoidance)
This system helps in avoiding the obstacles. A radar is fitted in the front and back of the car to focus ultrasonic waves and the distance of the object is calculated based on the time taken to return to receiver. The Obstacle detection and Collision avoidance are one and the same. They usually have it with brake support and the brakes are pre charged before their application. The collision system warns the user in case of any imminent collision by pre tensioning the seats, giving a visual and an audio warning and then if the user still doesn’t react, the car reacts on its own and applies the brakes hard. When the user does react by controlling the steering wheel left or right, then the brake assist is deactivated.

Parking Assist
This is one of the difficult task for a person. There are three main types of parking
- Parallel Parking
- Perpendicular parking
- Angular Parking
Out of these three, Parallel Parking is the most difficult and requires experience. Most of them fail in this and damage other cars. The other two are relatively easy and don’t require much skill and even a novice or a beginner can park the vehicle without any issues.
Here is a video of the VW Passat parking in action and also an ad for the Passat around the year 2011 mentioning the feature of Parking assist. These all fall under the bigger category of ADAS or Advanced Driver Assistance Systems.

Watch VW Passat CC – Auto Parking Assist 2.0
Watch Volkswagen Passat Advertisement.
So there you go. You learnt some basics of new automotive technology and how the future is going to be. Fascinated by the article? Leave Comments Below.
