Question: How to check if a particular website is using SHA1 or SHA2 Certificate? I would like to know the steps to check via web browsers and also using OpenSSL commands.
How to check Signature Algorithm of SSL certificate using OpenSSL Command?
The OpenSSL command shown below will fetch a SSL certificate issued to google.com and checks if the signature algorithm is SHA1 or SHA2.
$ openssl s_client -connect google.com:443 < /dev/null 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -text -in /dev/stdin | grep Signature Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
You can also use OpenSSL command to verify local web server certificate.
$ openssl x509 -text -in /etc/httpd/certs/server.crt |grep Signature Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
Check SSL certificate via Web Browser
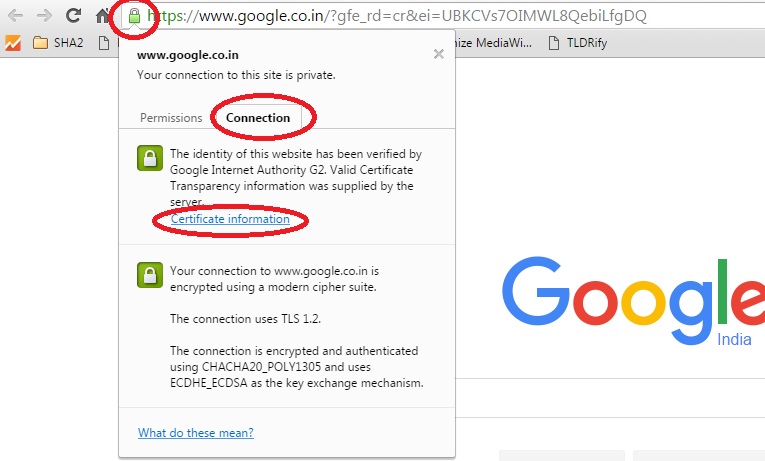
Google Chrome: After opening a website, click on the green lock icon next to the website URL in the address bar of the web browser. Click “Connection” > Certificate information.
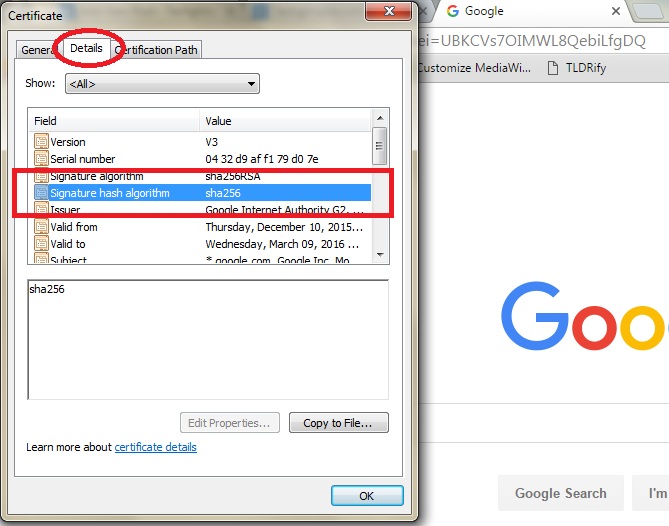
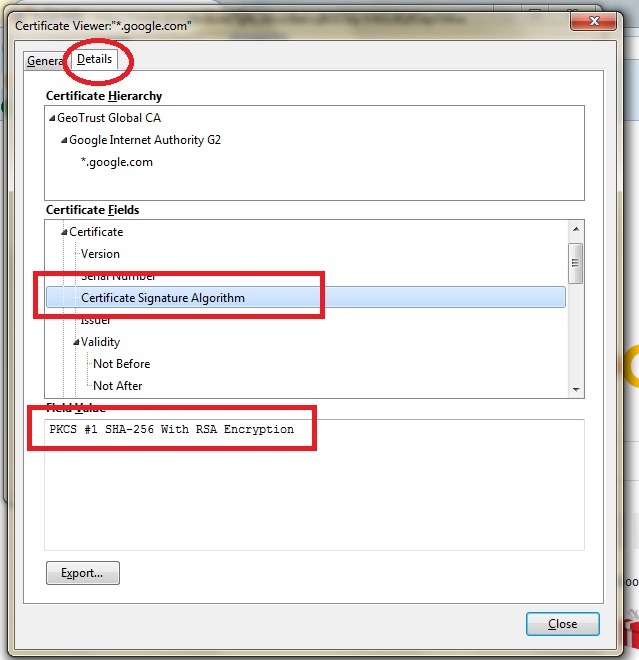
In the “Certificate” dialog, click “Details” and select “Signature hash algorithm” and lookout for the value.
On Firefox Browser:
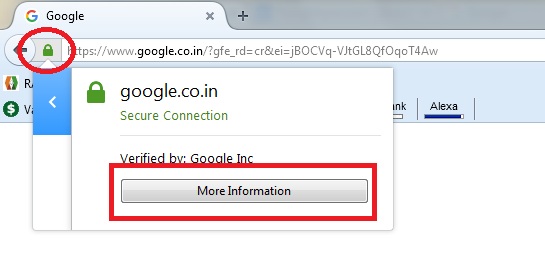
Click the lock icon next to the website URL in the address bar and click “More Information”
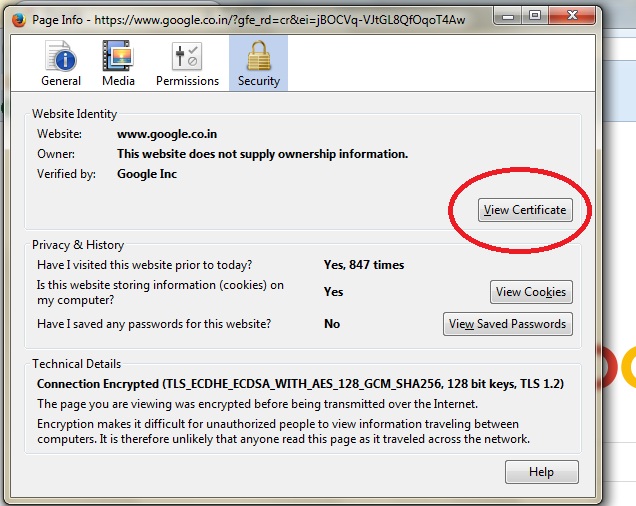
Click Security tab and “View Certificate” button.
In the “Certificate Viewer” dialog, click “Certificate Signature Algorithm” under “Certificate Fields” and lookout for the value.
On Internet Explorer:
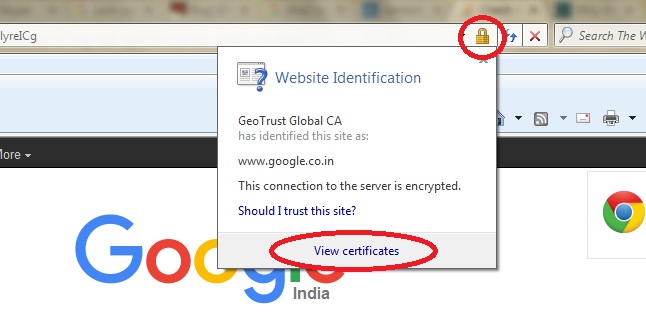
Click lock icon > View certificates.
In the “Certificate” dialog, click “Details” and select “Signature hash algorithm” and lookout for the value (refer the screenshot of Chrome).
This tutorial is a step by step guide to Generate SHA2 based Certificate using OpenSSL.


I’d put the message on top not on buttom. Message: SHA1 is obsolete and SHA256 is must.
As you suggested, now the message is at the top.
How can I determine the sha256 digest of the public key of an (issuer) certificate?
As quite some CAs re-use the public key of their issuer certs, the fingerprint changes, but the public key remains the same.
How can this be achieved with openssl?
For comparison in Java:
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance(“SHA256”, “BC”);
PublicKey pk = java.security.cert.Certificate.getPublicKey();
byte[] dig = md.digest(pk.getEncoded());
String sha256 = new BigInteger(1, dig).toString(16);