Ncdu is a disk usage analyzer based on ncurses. It provides a disk usage summary in a TUI (Text user interface) and finding large files and folders is really simple. ncdu is a curses-based version of the well-known “du” command in Linux, and provides a fast way to see what directories are using your disk space.
In order to install ncdu, you will first need to enable the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprises Linux) repo as shown below:
How to enable EPEL Repo:
For EL5:
[root@openstack export]# rpm -Uvh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpmFor EL6:
[root@openstack export]# rpm -Uvh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpmFor EL7:
[root@openstack export]# rpm -Uvh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-5.noarch.rpmHow to install ncdu
Once the EPEL repo is enabled, you can install ncdu with the following command:
Note: In case, if you don’t have ncurses installed, you can install it using ‘yum install ncurses‘.
[root@openstack export]# yum install ncdu
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, presto
Setting up Install Process
::::::::
::::::::
Installing : ncdu-1.11-1.el6.x86_64 1/1
Verifying : ncdu-1.11-1.el6.x86_64 1/1
Installed: ncdu.x86_64 0:1.11-1.el6
Complete!How to use ncdu
Run the below command to see the disk usage of present working directory (pwd).
[root@openstack ~]# ncduThe above command shows the disk usage under the root’s home directory.
To find the disk usage of specific directory, you can either navigate to the directory and issue the command ‘ncdu’ or issue the command ‘ncdu /lib/’
[root@openstack lib]# ncduor
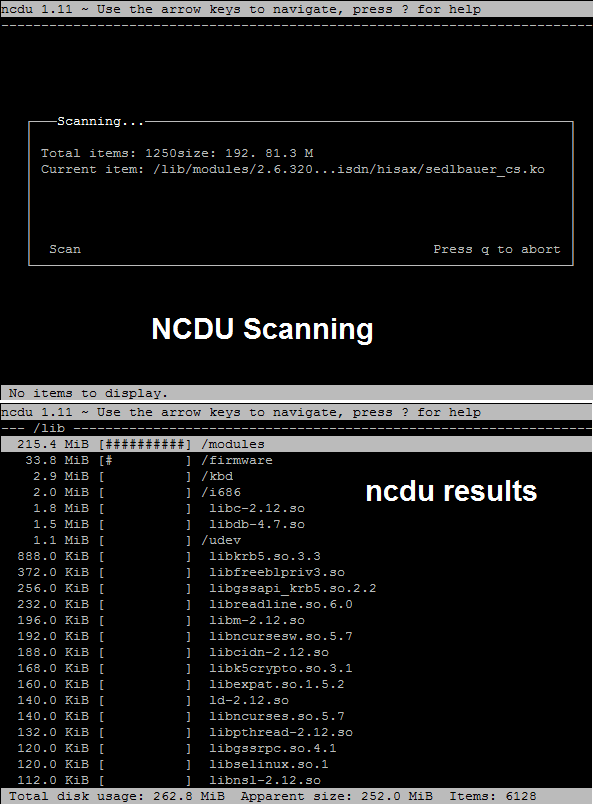
[root@openstack ~]# ncdu /lib/You can see the scanning of directories and the results in the below image:
Scan full filesystem
[root@openstack ~]# ncdu -x /Keyboard shortcuts
? for help up, k Move cursor up down, j Move cursor down right/enter Open selected directory left, <, h Open parent directory n Sort by name (ascending/descending) s Sort by size (ascending/descending) g Show percentage and/or graph i Show information about selected item r Recalculate the current directory q quit