The worlds top Operating system Android comes a log way. Android is an operating system based on the Linux kernel, and designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Initially developed by Android, Inc., which Google backed financially and later bought in 2005, Android was unveiled in 2007 along with the founding of the Open Handset Alliance: a consortium of hardware, software, and telecommunication companies devoted to advancing open standards for mobile devices. The first Android-powered phone was sold in October 2008. The Open Handset Alliance (OHA) is a consortium of 84 firms to develop open standards for mobile devices. Member firms include Google, HTC, Sony, Dell, Intel, Motorola, Qualcomm, Texas Instruments, Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, T-Mobile, Sprint Corporation, Nvidia, and Wind River Systems.
Android history at a glance- Going back into the past.
( Rewinding<<<<<<)
<We are now in the past!>
Android, Inc. was founded in Palo Alto, California in October 2003 by Andy Rubin (co-founder of Danger), Rich Miner (co-founder of Wildfire Communications, Inc.), Nick Sears (once VP at T-Mobile), and Chris White (headed design and interface development at WebTV) to develop, in Rubin’s words “smarter mobile devices that are more aware of its owner’s location and preferences”.

ANDROID 1.0 (Codenamed Astro)
The first Android phone was released back in 2008 when Symbian and Windows Mobile were dominating the market. Android was just a concept back then. Rubin rewrote the Linux Kernel to make it look like it but in fact it is just one strand which can neither be replicated into a Linux Kernel nor into a kernel of its own, its in the middle and this formed the framework of Android. Though Android Inc and Android were not famous by then, the first device to feature Android was the HTC Dream. The features back then were very limited and you couldn’t even edit the ringtone of the phone. Then Google acquired Android Inc. and were working on more features to improve the platform and be a more severe competition to the Nokia owned Symbian. Symbian was dominant in the market and was holding a majority of share and phones and Nokia was a kingmaker in Smartphone industry back then.

Not many of you’ll recognize this device as this was not a very popular device due to highly popular Symbian.
With the advent of technology and more years to follow, the Google based Operating System was sure incorporating some research and underlying hood developments. The Linux based kernel was improved. The pull up app drawer was further improved. Some cosmetic changes were also incorporated.
ANDROID 1.5 (Cupcake)
The alphabetical ordering of the versions of Android start with this particular version. Android 1.5 went through many years of research and developers to incorporate some of the minor changes which were necessary to help improve the devices. The update at that time was major! This version came with ability to change wallpapers, change ringtones, etc. to name a few. The introduction of Android market came with this version where the apps can be downloaded and bought. This was one of the more sought features which changed the way people looked at android.

The first device to feature this version of Android was the HTC Magic.
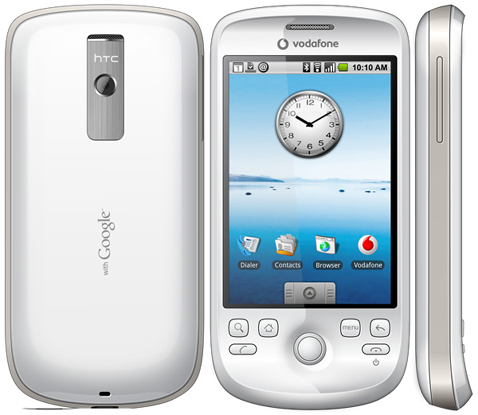

Android 1.6 (Donut)
The next version of Android is the Donut. The first version is Cupcake which starts with a C, so the next version in the list of alphabets should start with a D hence Donut. Donut improved features like improved quality of videos uploaded to websites like YouTube etc. This version of Android is only feature update and not major changes to the UI as such. It fixed reboot errors in the OS as well as revamped photo and video features (i.e. camera interface) and better search integration. It also added support for larger screen size, and is the first version to offer Google turn-by-turn navigation feature.

The first device to feature this update was the Motorola Devour.
ANDROID 2.0/2.1 (Éclair)
WIth the next version that is éclair, the advent of live wallpaper came. This was the version which caused the sales of Symbian to go down and made people to buy android. There were far more improvements to this version than the jump from 1.5 to 1.6. Some of the features are:
* Expanded Account sync, allowing users to add multiple accounts to a device for synchronization of email and contacts
* Microsoft Exchange email support, with combined inbox to browse email from multiple accounts in one page
Bluetooth 2.1 support
* Ability to tap a Contacts photo and select to call, SMS, or email the person
*Ability to search all saved SMS and MMS messages, with delete oldest messages in a conversation automatically deleted when a defined limit is reached
* Numerous new camera features, including flash support, digital zoom, scene mode, white balance, color effect and macro focus
* Improved typing speed on virtual keyboard, with smarter dictionary that learns from word usage and includes contact names as suggestions
* Refreshed browser UI with bookmark thumbnails, double-tap zoom and support for HTML5
* Calendar agenda view enhanced, showing attending status for each invitee, and ability to invite new guests to events
* Optimized hardware speed and revamped UI
* Support for more screen sizes and resolutions, with better contrast ratio
* Improved Google Maps 3.1.2
* MotionEvent class enhanced to track multi-touch events
* Addition of live wallpapers, allowing the animation of home-screen background images to show movement

The first phone to feature this was the Motorola Droid after which Android came to be known as Droid. This was the phone which helped in Android’s course of success due to its build quality which comes after Nokia. The build quality and its ability to handle the software was what enticed people.

ANDROID 2.2-2.2.1 (FroYo)
The Android 2.2 FroYo saw the replacement of the pull up app drawer to a 4×4 grid design. The app drawer’s animation is still the same. When you click on the 4×4 grid, all the apps come into view with a pull up only. The first device to feature this was the HTC Nexus One. The Nexus One was a device by HTC and is Google branded. Most of the features were improved that came in Éclair. FroYo stands for Frozen Yoghurt (btw).
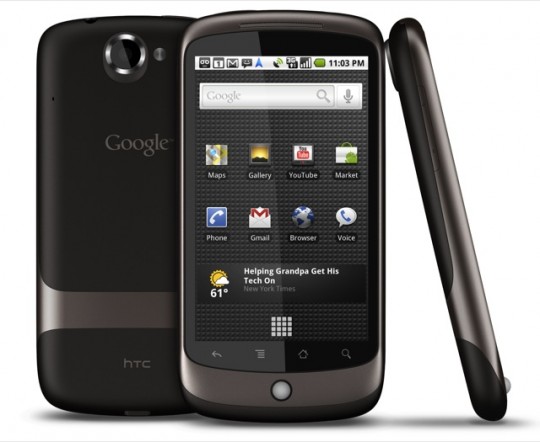


Android 2.3.7 (GingerBread)
This version of Android was next to Android 2.2 FroYo. It was an instant success. The main feature in this version was connectivity- it came with NFC connectivity, Bluetooth3.0, etc. The first device to support this was Samsung Nexus S. There are so many versions of GingerBread in the market. It was the most stable version of Android.


ANDROID 3.0-3.2 (Honeycomb)
This version is Strictly for Tablets. This version only enjoyed a little reigning. The first tablet to feature this was the Motorola Xoom.

ANDROID 4.0-4.0.4 (ICS or Ice Cream Sandwich)
This version of Android is a custom version which incorporates both Honeycomb as well as it is available for Smartphones. With the changes in UI, and improvements under the hood of Android, this version was sure to be a success. The features of this version are as follows:
Soft buttons from Android 3.x are now available for use on phones
* Separation of widgets in a new tab, listed in a similar manner to apps
* Easier-to-create folders, with a drag-and-drop style
* A customizable launcher
* Improved visual voicemail with the ability to speed up or slow down voicemail messages
* Pinch-to-zoom functionality in the calendar
* Integrated screenshot capture (accomplished by holding down the Power and Volume-Down buttons)
* Improved error correction on the keyboard
* Ability to access apps directly from lock screen
* Improved copy and paste functionality
* Better voice integration and continuous, real-time speech to text dictation
* Face Unlock, a feature that allows users to unlock handsets using facial recognition software
* New tabbed web browser under Google’s Chrome brand, allowing up to 16 tabs
* Automatic syncing of browser with users’ Chrome bookmarks
* A new typeface family for the UI, Roboto
*Data Usage section in settings that lets users set warnings when they approach a certain usage limit, and disable data use when the limit is exceeded
* Ability to shut down apps that are using data in the background
* Improved camera app with zero shutter lag, time lapse settings, panorama mode, and the ability to zoom while recording
* Built-in photo editor
* New gallery layout, organized by location and person
* Refreshed “People” app with social network integration, status updates and hi-res images
* Android Beam, a near-field communication feature allowing the rapid short-range exchange of web bookmarks, contact info, directions, YouTube videos and other data
* Support for the WebP image format, to name a few.
the first device to feature this update was the Galaxy Nexus.


<Coming back to the present>
The Nexus One is a device which is still enjoying developer support. It can be updated to the Next version of Android ie. Jelly bean also. Such a property is what people love in Android the most and move on to Open Source. The next version of Android is the Jelly Bean.
ANDROID 4.1-4.3 (Jelly Bean)
This version of Android brought with it many changes as to how Android feels or glides. It is an update over ICS and it brought about Project Butter which uses touch anticipation, triple buffering, extended vsync timing and a fixed frame rate of 60 fps to create a fluid and “buttery-smooth” UI. The app open and runtimes were considerably reduced and the lag was considerably reduced. Jelly Bean takes the connectivity to another level. The first device to feature this update was the Nexus 7.


<Into the future>
ANDROID 4.4 (KitKat)
There were rumours and news that Google might name the next version as Key Lime Pie, but fortunately it was named after a famous chocolate treat, KitKat! This version of Android brings about many changes to the devices and how they are run. The first and most important change is the runtime environment. IT is said to use ART type of processing. The following are some of the many features of the latest iteration of Android.
* Refreshed interface and revised framework for UI transitions
* Performance Optimization for devices with lower specifications and Low RAM
* Modification in Printing framework
* NFC Host Card Emulation
* Web Views based on Chromium (feature parity with Chrome for Android 30)
* Expanded Notification listener services
* Public API for text messaging clients and power to select a default SMS app
* Storage access framework
* Sensor batching, Step Detector and Counter APIs
* “Immersive” full screen mode and software buttons, status bar access with edge swipe gesture
* Audio tunneling, audio monitoring, loudness enhancer
* Built-in functionality for screen recording
* Native infrared blaster API
* Expanded accessibility APIs, system-level closed captioning settings
* New runtime virtual machine, ART
* Bluetooth Message Access Profile (MAP)
As said earlier, the Android 4.4 was thought to be Key Lime Pie at first and with a version number of 5.0 but Google at its I/O conference told clearly that this wasn’t the case and that they have reconsidered the name to be KitKat– after the popular chocolate by Nestle. The first device to feature this update will be the Nexus 5.

Now, as Google has decided to name its updates in the Alphabetical order, we don’t know what will happen if the alphabets come to an end. Let’s pray that doesn’t happen!

