Windows Phone OS is the youngest and latest OS in the market. Majority of manufacturers choose Android but only few choose Windows Phone platform as their main OS. In this aspect, I salute you thee Nokia. Nokia is continually putting in more effort and helping in expansion of the WP platform. The platform would’ve otherwise been dead if Nokia hadn’t chosen this. It would be more like MeeGo– having an ending as soon as the beginning. This is Shiva and I am bringing you my 100th article with a bang! My favorite OS, its history and a struggle for the third position from the World number 1. The article is arriving late just like how Windows Phone arrived late. But as Super star Rajinikanth (Indian actor) says “Late ah vanthalum Latest ah irukum” (Means, even if its late, it’s the latest)
Lets start from when Symbian and Windows Mobile were very popular, that none of the other operating systems could match them to give them a scare!
<<<<<<<<Rewinding to the past.
Windows CE
Microsoft started its research on handheld devices and the work started on 1990 and Microsoft introduced Windows CE. At first, the User Interface and OS were developed separately and the UI was called WinPad. ( later it became Microsoft at work for handheld). The Windows CE was based on Windows 95 which had a wonderful pen support. But the handheld got some touchscreen driver problem and was not introduced into the consumer market. But Windows CE was the first ever touch screen phone to be introduced theoretically but due to the issues, it wasn’t released. Motorola got that award rather. The alpha and beta versions were released and they saw high cost and performance issues.
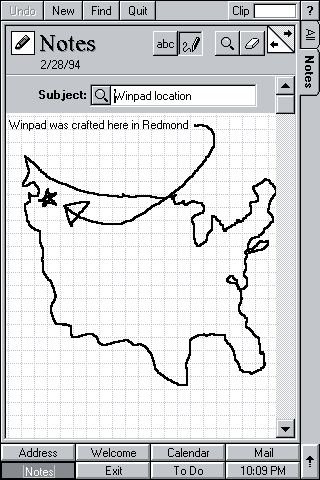
Pocket PC 2000
This was codenamed “Rapier” was released on April 19, 2000. It was based on Windows CE 3.0 and it runs on top of Palm PCs. It was intended for Pocket PC devices. The only resolution supported to be 240×320 (QVGA). Removable storage card formats that were supported were CompactFlash and MultiMediaCard. At this time Pocket PC devices had not been standardized with a specific CPU architecture. ARM architecture and Infrared Beaming were among the initial hardware features. The initial release had Pocket Office and Windows Media Player. Character recognition were highly supported and this allowed Notes to be written and distinguished easily.
Pocket PC 2002
There was no 2001 version. The development took that long and the improved features and the UI were changed in this version. It is codenamed “Merlin“. It was released in October 2001. It was based on Windows XP. There was support for Microsoft reader 2, DRM support, WMP 8 with streaming capability. The other features were WAP and performance upgrades.

Windows Mobile 2003
Codenamed “Ozone“, this was the transition from Pocket PC to Windows Mobile. Pocket PC range of devices include those old handhelds such as HP iPAQ which were running the older version of Windows.But this was further improved to support a wide range of devices and improved UI system. There was also a second edition released termed SE. The first version saw enhanced communication interface which supported Bluetooth beaming, headset support and add-on keyboards. The other features include a vCal and vCard support, Pocket Internet explorer, Pocket outlook and SMS Reply option.
Windows Mobile 2003 SE
The Second Edition or SE builds over the first version. It was released on March 24, 2004. This was the last version to allow users to backup and restore using ActiveSync. An array of new screen resolutions 640×480, 176х220, 240×240, and 480×480 debuted. Support for Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and Portrait and landscape modes in Pocket Internet Explorer were also supported.
Windows Mobile 5.0
Codenamed “Magneto” and was released in the Microsoft’s Mobile and Embedded Developers Conference 2005 held at Las Vegas between May 9 to May 12, 2005. A lot of features were incorporated in this version. The minimum requirement was at least 64MB of RAM. There was enhanced Bluetooth support, ActiveSync 4.2 for syncs, Microsoft Office mobile, QWERTY keyboard, DirectDraw, DirectShow, And visual Caller ID support. DirectDraw is the native graphics accelerator which is similar to DirectX now. This was the penultimate version of Windows Mobile.
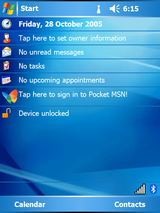
Windows Mobile 6.0
Windows Mobile 6 was codenamed Cross Bow. It was released on February 12, 2007 at the 3GSM World Congress 2007. This was the first release that had three versions of the OS like Normal Windows. They are:
- Windows Mobile 6 Standard for Smartphones (phones without touchscreens),
- Windows Mobile 6 Professional for Pocket PCs with phone functionality, and
- Windows Mobile 6 Classic for Pocket PCs without cellular radios
This was based on Windows CE 5.2 and it was also to be similar in design to the then newly released Windows Vista. It builds upon Windows Mobile 5 and has same design but with improved stability. Office Mobile OneNote was added and support was also added for HTML email. Communication interface and abilities were further enhanced such as VoIP with AEC (Audio Echo cancelling) and MSRT Audio codec.
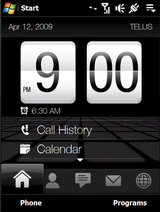
Windows Mobile 6.1
Windows Mobile 6.1 was released as a minor upgrade over the Windows Mobile 6 platform and included performance upgrades and bug fixes. It featured a new start screen and an interactive Getting started wizard which are till date used in many of the Android phones and others as well. Other changes include the Threaded view. There were not that much visual changes but there were changes as to how builds were to be named. Instead of using 4 digits to the build, Microsoft decided to use 5.
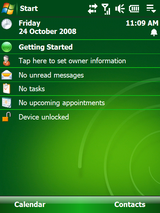
Windows Mobile 6.5- 6.5.5
WM 6.5 is the latest and last version of the WM series and which was intended to bridge the gap between WM 6.1 and 7. But WM 7 wasn’t developed and it was renamed Windows Phone 7. Windows Mobile 6.5.3 was the stable release and Windows Mobile 6.5.5 was the unstable release and wasn’t released publicly. There were changes in the UI and after a definite period of servicing, the oxygen mask (support) was removed and WM 6.5 was officially dead.
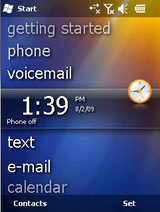
Transition from Windows Mobile to Windows Phone
Windows Phone 7
Windows Phone 7 (as it is named now) was previously thought to be Windows Mobile 7. The UI was completely overhauled and Microsoft developed something called as the Modern UI or the Metro UI. The phone’s minimum requirements were 256MB RAM. The phone had a power button and a volume rocker present. It was introduced in the Mobile World Congress at Barcelona. Windows Phone initially supported twenty five languages and an inclusion of the Phone Store was an added bonus for app downloads. The phone supported Live tiles which were not customizable and were rather static. There was no notification center on the device, No file manager and connectivity options were quite limited. There was another update that was called NoDo which included improved startup times, Copy and paste, etc.
Related :Top 15 Latest Gadgets on Display at Mobile World Congress, Barcelona
Windows Phone 7.5 (Mango and Tango)
This was the first update to the Windows Phone 7 series. This update was codenamed Mango. The update incorporated a lot of features that were not present in WP7. They include*:
Messaging and social integration
- Dynamic Live tile information
- Twitter and LinkedIn integration in the People hub.
- Groups: organize contacts by groups which can also be pinned on the start screen.
- Contact cards now include all the contacts conversation history (SMS, emails, MMS, Messenger, etc.)
- Facebook Places check-in support.
- Windows Live Messenger and Facebook Chat integration.
- Threads: all messaging communication organized in a single thread (Messenger, SMS, MMS).
- Threaded email conversations support.
- Outlook tasks support.
- Facebook events integrated into the calendar.
- Linked email accounts: multiple email accounts can be combined and linked into one inbox.[5]
- Built-in voice-to-text/text-to-voice functionality, which will allow for hands-free texting or chatting.
- Server search for Exchange.
- Information Rights Management support for emails and Office documents.
- Visual Voicemail
Also Read : Windows Phone OS beats iOS in Latin America!
Search/Bing
- Bing Vision: barcode, covers, posters, products scanning, and OCR text translation.
- Bing Audio / Music: Shazam-like audio recognition.
- Bing Local Scout: “around me” business and POI locator.
- Bing Quick Cards: product/media information, reviews.
- Bing Search: indoor maps (US only), image search results, third-party app integration.
- Bing Maps: turn-by-turn navigation, voice guidance
Office
- Skydrive and Office 365 documents sync (PDF also supported).
- Excel Mobile now supports adding additional macro functions.
- Microsoft Lync support via downloadable app.
- Added “To-Do” option when editing OneNote pages.
- Removed ability to edit Office documents from versions older than Office 2007.
You Might Like : Rumour : Micromax going the Windows way?
Photo management
- People / Groups gallery with Skydrive and Facebook sync.
- People tagging in the photos with Skydrive and Facebook sync.
- Photo auto-fix – automatically improves sharpness, brightness, etc.
- Pictures tile is now animated.
- Video sharing via MMS, Facebook, Skydrive, and email.
- Twitter integration—Tweet your pics
- Integration with the People Hub.
- Quick access to the Camera Roll.
- When you choose a photo from within an app, you can now pick from online albums on Facebook or SkyDrive, not just pictures saved on your phone.
- Pin any album to Start, including Facebook albums.
Multimedia
- Zune SmartDJ mix support.
- Artist picture now displays on lock screen when music is played.
- UI change of the media controls on the lock screen.
- Ability to control video aspect ratio during playback.
- Single music track repeat without having to pin it on the start screen.
- Podcast downloads / subscriptions over the air (US only).
- Open / play media content by voice.
- Ability to create and save playlists.
Marketplace
- Revamped Marketplace UI and search.
Camera
- UI changes (new icons + added arrow icon on the lower left of the viewfinder to indicate camera roll).
- Settings are now saved when the Camera application is closed.
- Disable/enable shutter sound.
- Support for front facing camera.
- Touch focus and capture—Tap any spot on the screen to focus there and take the shot. (This varies according to hardware—some phones will have tap-to-capture but will still automatically center focus.)
- Review pictures above the lock—Snap a photo when your phone is locked, then take a peek at it above the lock. You’ll only be able to get to photos you just took—better for security.
- Changes for portrait orientation—Now, when you take a picture in portrait orientation, you’ll see it in portrait orientation when you review it.
Also Read : Android evolution at a glance- History of the world’s top OS
Games
- Redesigned Games hub with integrated 3D avatar and avatar customization.
- Friends and achievements now integrated in the hub.
- Fast Async for multiplayer games.
Internet Explorer 9 Mobile
- Hardware-accelerated rendering.
- Support for HTML5 audio and video playback.
- Background HTML5 audio playback.
- Geolocation support.
- New JavaScript engine.
- New UI with URL bar at the bottom of the screen.
- URL bar is now available in landscape mode.
- Removal of Find on Page feature
- Moved the “tabs” button to a menu item under the application bar
Security
- Voice commands are now disabled when the device is locked.
- Complex (alpha-numeric) PIN support.
Suggested Post : Get Complete History of HTML5 and its Scope [2013 HTML5 Infographic]
Other changes
- Internet sharing
- Battery saver: phone automatically disables power consuming services and applications running in the background if the battery is low. Also predicts time remaining on battery.
- Ringtone manager with custom and downloadable ringtones.
- The “People” tile has been reworked and is animated differently than before.
- Search icon and quick jump list added to the application list.
- Support for 16 new languages: Czech, Danish, Hungarian, Dutch (Netherlands), Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese (Brazil, Portugal), Finnish, Swedish, Greek, Russian, Korean, Chinese (Traditional, Simplified), Japanese.
- East Asian handwriting recognition.
- Support for new languages and emoticons in on-screen keyboard.
- Hidden WiFi network support.
- Qualcomm MSM7X30 and MSM8X55 support.
- Programs menu will have alphabetical options similar to the people functionality
- Power off now requires a swipe down gesture after holding down the power button for a few seconds.
- Removal of “soft-on” alarm feature
- Modification of alarm sleep interval
Development API changes and additions
- Third-party application multi-tasking and fast application switching.
- Support for background tasks and services/agents.
- Expanded live tiles that can be updated without network connection and can have two sides which flip periodically.
- App Connect: third-party applications can integrate with Bing search, have multiple live tiles, and can have push notifications that link deep (“Deep Toast”) into various parts of the application directly.
- Optional 32 bit color support for Silverlight applications with hardware dithering.
- Silverlight 4 support.
- Silverlight + XNA support in the same application screen.
- Raw camera feed access for third-party applications.
- New sensor API combines compass, gyroscope, and accelerometer.
- Improved Listbox control with better scrolling performance.
- Improved WebBrowser control with IE9 rendering engine and system-wide cookies access.
- Clipboard API.
- Hardware-accelerated video decoding in the MediaPlayer control.
- TCP/IP and UDP sockets support.
- Embedded database with LINQ (based on SQL Server Compact 4.0 engine, but without direct SQL execution).
- Background file transfer agent.
- Generational garbage collector.
- NEON/SIMD support for XNA applications
*- Features as in Wikipedia. Thank you, Wikipedia.
Mango was a relatively minor update to Tango. It included bug fixes and performance improvements.
Windows Phone 7.8
This was an update that was released after Wp7 released on October 29. It was an update for existing Wp7 users in order to control their fury. It included customizable tiles and ability to resize them. There were three sizes incorporated small medium and large. The update to Windows Phone 8 was not permitted because of Microsoft saying that the hardware was not sufficient enough.
Windows Phone 8
This is the latest version of the OS and is said to be based on Windows 8. Or, the other way around, the version was based on the NT Kernel and included support for multi cores, card slot support, Easy porting as the apps were to be written in C/C++. All these features made this OS very popular with the developer community. But there were restrictions placed. Hardware restrictions included necessary placing of three capacitive buttons below the screen. They include the Back , start and the search button which you can find in almost every Windows 8 Phone. The limitation of this phone was 512MB RAM. i.e. the Minimum RAM Required was 512MB. The power button was placed in the middle of the right hand side and the volume rockers on the top. The UI was very well enhanced to feature easy use and other improvements under the hood. Microsoft released three updates- GDR, GDR2 and the GDR3 for the devices running WP8. They incorporate a lot of features which was missing from the OS in the beginning and from the transition from WP7 to WP8. Nokia Lumia phones get additional Nokia goodies which are not present in the GDRs. That is the added advantage of having a Nokia Lumia (Source: Proud Nokia Lumia owner).
Windows Phone 8.1 is in the makes and as the further details are not known, it is not present in this article. The OS has come a long way and is intending to go a long way. The OS is reliving again and again as all of the standard features that came with Windows Mobile got into WP7 but when the developers went ahead with WP8, they “ran out of time” and most of the features are still missing which should be a standard part of the OS. Nokia has done a lot for Microsoft and it is now Microsoft’s turn to do the same for Nokia. Come on Microsoft, we are expecting more!

